The two-dimensional code scanner market is experiencing significant growth driven by the increasing adoption of digital technologies across various sectors. As businesses and consumers alike seek more efficient ways to manage information and transactions, two-dimensional codes, commonly known as QR codes, have gained popularity for their ability to store large amounts of data in a compact format. This technology is not only facilitating seamless interactions between customers and businesses, but it is also enhancing inventory management, product tracking, and marketing strategies. The convenience and versatility offered by two-dimensional code scanners are propelling their integration into retail, healthcare, logistics, and numerous other industries.
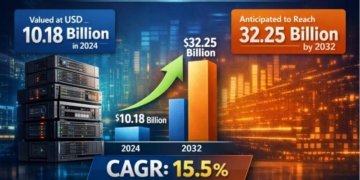
The market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.30% from 2025 to 2032, reflecting the increasing demand for automation and digital solutions. As more consumers become familiar with scanning codes for information retrieval, payment processing, and promotional activities, the reliance on two-dimensional code scanners is expected to expand. Moreover, advancements in scanning technology, such as improved accuracy and speed, are further contributing to market growth. By 2032, the two-dimensional code scanner market is expected to surpass a valuation of several billion dollars, indicating robust future prospects. This growth trajectory underscores the importance of two-dimensional code scanners as integral tools for businesses aiming to enhance customer engagement and operational efficiency in an increasingly digital world.
You can access a sample PDF report here: https://www.statsndata.org/download-sample.php?id=601
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Two-dimensional Code Scanner Market Poised for Explosive Growth Amidst Technological Advancements
Market Overview and Recent Developments
The two-dimensional code scanner market is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demand for efficient data capture and management solutions across various sectors. These innovative devices, including QR code scanners, barcode scanners, and mobile code scanners, have become integral to operations in retail, healthcare, logistics, and beyond. The scope of the two-dimensional code scanner market extends to a wide array of applications such as inventory management, customer engagement, and contactless payment systems.
Recent breakthroughs in scanning technology, including enhanced optical scanning capabilities and the integration of artificial intelligence, have significantly boosted the functionality of two-dimensional code scanners. Strategic partnerships between technology firms and industry leaders are further catalyzing market growth, allowing companies to leverage cutting-edge innovations to meet consumer needs. As businesses increasingly recognize the advantages of using QR code scanners for marketing and operational efficiency, the demand for high-quality digital scanners has surged.
Executives, investors, and decision-makers should note that the two-dimensional code scanner market is not just expanding; it is transforming the way businesses operate. The convergence of digital technology with traditional practices is creating actionable insights that can drive competitive advantage, streamline processes, and enhance customer experiences.
Key Growth Drivers and Trends
Several key drivers are propelling the growth of the two-dimensional code scanner market. Sustainability and digitization are at the forefront, as businesses seek to minimize waste and improve efficiency. The shift in consumer expectations towards seamless, contactless shopping experiences has also increased the reliance on mobile code scanners and QR code readers.
Transformative trends such as the integration of AI into scanner apps are enhancing the capabilities of two-dimensional code scanners. AI algorithms can optimize scanning speed and accuracy, making it easier for users to scan multiple QR codes quickly. Additionally, product customization is gaining traction, with businesses seeking tailored solutions that fit their specific operational needs. Emerging technologies like IoT and blockchain are expected to further revolutionize the industry, paving the way for unprecedented levels of data security and interoperability.
In this evolving landscape, it is crucial for businesses to stay informed about the latest developments in two-dimensional code scanning technology. Understanding the features to look for in a digital scanner can empower decision-makers to choose the best solutions for their operations.
Market Segmentation
The two-dimensional code scanner market can be segmented into distinct categories based on type and application.
Segment by Type
1. Stationary Reading
2. Handheld Reading
3. Others
Segment by Application
1. Industrial
2. Daily Use
3. Others
Stationary reading devices are typically used in retail and manufacturing environments, where constant scanning is required. Handheld reading scanners, including mobile code scanners, offer versatility for various applications, from logistics to point-of-sale transactions. The daily use segment encompasses personal use cases, such as scanning QR codes for promotions or information.
Understanding these segments helps businesses tailor their scanning solutions to meet the specific needs of their operations and customer interactions.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape of the two-dimensional code scanner market is characterized by several leading players committed to innovation and customer satisfaction. Key companies include:
Cognex: Known for its advanced vision systems, Cognex has recently launched new data matrix scanners that enhance accuracy in inventory management.
Keyence: This company continues to expand its offerings with cuttingedge optical scanners designed for highspeed applications in manufacturing.
Cilico: Cilico has introduced new handheld QR code scanners that focus on userfriendly interfaces and affordability.
Sanpo: Sanpo is pioneering contactless scanners that prioritize health safety, particularly in retail environments.
Honeywell: Honeywell’s latest scanner app integrates with cloud services, allowing for seamless data management and analysis.
RTscan: RTscan is focusing on developing AIdriven scanners that improve efficiency in logistics operations.
Newland AutoID: This company is expanding its product line with innovative solutions tailored for the healthcare sector.
Riotec: Riotec has launched new data matrix scanners aimed at enhancing operational productivity in industrial settings.
Godeland: Godeland’s recent partnerships with software developers are driving the integration of code readers into various applications.
Denso ADC: Denso ADC is making strides with its latest mobile code scanners, designed for quick and efficient customer service applications.
These companies are at the forefront of the two-dimensional code scanner market, continually pushing the boundaries of technology and customer service.
Opportunities and Challenges
The two-dimensional code scanner market presents numerous opportunities for businesses willing to innovate. Untapped niches, such as the integration of code readers into mobile applications and the growing demand for contactless solutions, provide avenues for expansion. Understanding evolving buyer personas, particularly among younger consumers, can help businesses tailor their offerings to meet changing preferences.
However, challenges remain. Regulatory hurdles and supply-chain gaps can impede growth. To navigate these obstacles, companies should invest in robust supply chain management strategies and stay informed about regulatory changes affecting the industry.
Technological Advancements
The landscape of two-dimensional code scanners is being reshaped by cutting-edge technologies. Artificial intelligence is enhancing the performance of digital scanners, allowing for faster and more accurate readings. Digital twins and IoT are facilitating real-time data analysis, improving inventory management and operational efficiency. Virtual reality is also emerging as a tool for training personnel on effective scanning techniques.
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize the security aspect of code readers, providing a tamper-proof method of capturing and storing data. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly influence the future of the two-dimensional code scanner market.
Research Methodology and Insights
At STATS N DATA, we employ a comprehensive research methodology to deliver robust insights into the two-dimensional code scanner market. Our approach encompasses both top-down and bottom-up methodologies, ensuring that we capture a holistic view of market dynamics. Primary and secondary data collection methods are utilized to enrich our findings, while multi-layer triangulation adds a layer of credibility to our insights.
We are committed to providing data-driven insights that empower businesses to make informed decisions in the rapidly evolving landscape of two-dimensional code scanners.
This press release aims to position STATS N DATA as a thought leader in the two-dimensional code scanner market, highlighting our expertise and commitment to delivering actionable insights for executives and decision-makers.
Get 30% Discount On Full Report: https://www.statsndata.org/ask-for-discount.php?id=601
In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, a key player in the retail sector faced a significant challenge. Their traditional methods of inventory management were falling short in efficiency and accuracy, leading to frequent stock discrepancies and customer dissatisfaction. As the company expanded its operations across multiple regions, the existing system struggled to keep up with the growing demands of real-time data analysis and product tracking. With competition intensifying, the company knew it had to innovate or risk losing its market position. The need for a more reliable and effective solution became increasingly urgent, prompting the leadership team to seek out advanced technologies that could streamline operations and enhance customer experience.
Recognizing the potential of two-dimensional code scanning technology, the company turned to STATS N DATA analysis for guidance. This analytical approach involved a comprehensive evaluation of the current inventory management processes, integrating cutting-edge data analytics with actionable insights. The analysis revealed critical pain points, such as the lack of real-time inventory visibility and inefficient manual stock counting methods. Building upon these findings, STATS N DATA developed a groundbreaking strategy that involved the implementation of a sophisticated two-dimensional code scanning system. This new system allowed for instantaneous product identification and tracking, significantly reducing human error and improving data accuracy. By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities, the company could now monitor inventory levels in real time and make informed decisions based on precise data.
The results of this strategic overhaul were remarkable. Within months of implementing the new two-dimensional code scanning technology, the company experienced a substantial increase in market share, as customers gravitated toward the enhanced shopping experience. The new system improved operational efficiency by streamlining the inventory management process, reducing the time spent on stock counts by over 50 percent. This newfound efficiency translated into higher revenue, with the company reporting a 30 percent increase in sales during the first quarter following the implementation. The combination of accurate inventory tracking and improved customer satisfaction fostered a more loyal customer base, further solidifying the company’s position in the market. The success story of this key player serves as a testament to the transformative power of innovative technology and data-driven strategies in overcoming contemporary challenges.
For customization requests, please visit: https://www.statsndata.org/request-customization.php?id=601
Q: What is a two-dimensional code scanner?
A: A two-dimensional code scanner is a device or software application that reads two-dimensional barcodes, commonly known as QR codes or data matrix codes. Unlike traditional one-dimensional barcodes that only store information in a linear format, two-dimensional codes can store a significant amount of data in both horizontal and vertical dimensions. This allows for the encoding of various types of information, such as URLs, text, contact information, and more. Two-dimensional code scanners can be found in various forms, including handheld devices, fixed-mounted scanners, and mobile applications, making them versatile tools for a variety of industries.
Q: How does a QR code scanner work?
A: A QR code scanner works by using a camera or imaging sensor to capture an image of a QR code. The scanner processes this image using a decoding algorithm that interprets the pattern of black and white squares, which represent data. The scanner first locates the position and orientation of the QR code, then extracts the data encoded within it. This data might include links to websites, text, or other information. The decoded information is then displayed to the user or used in an application, allowing for quick access to the linked data or action.
Q: What are the benefits of using a barcode scanner?
A: Using a barcode scanner offers several benefits, including increased efficiency, accuracy, and speed in data entry. Barcode scanners eliminate the need for manual data entry, reducing human error and ensuring data integrity. They also speed up the checkout process in retail environments, streamline inventory management, and facilitate quick data retrieval in various applications. Furthermore, barcode scanners can improve customer experience by enabling fast and efficient service. Overall, the use of barcode scanners can lead to cost savings and better resource management for businesses.
Q: Can I use my phone as a mobile code scanner?
A: Yes, you can use your phone as a mobile code scanner. Most smartphones come equipped with cameras and can run applications that decode QR codes and other two-dimensional codes. There are numerous apps available on both iOS and Android platforms that allow users to scan codes. Many of these apps are free and easy to use, making it convenient for individuals and businesses to access information encoded in two-dimensional codes without the need for dedicated hardware. Some smartphones even have built-in scanning capabilities within their camera apps.
Q: What features should I look for in a digital scanner?
A: When selecting a digital scanner, there are several key features to consider. First, look for scanning speed and accuracy, as these will affect how efficiently you can process codes. Consider the scanning range; some scanners work better up close, while others can scan from a distance. Compatibility with various code types, including QR codes and data matrix codes, is important as well. Additionally, consider the scanner’s durability, especially if it will be used in a rugged environment. Software features such as data management capabilities and integration with existing systems can also enhance the scanner’s utility. Finally, battery life and ease of use are practical considerations that can influence your choice.
Q: How do I choose the right scanner app?
A: Choosing the right scanner app involves assessing your specific needs and the features offered by various apps. Start by determining what types of codes you need to scan and ensure the app supports those formats. Look for apps with good user reviews and a proven track record of reliability. Features such as batch scanning, history storage, and integration with other applications can also be beneficial. Additionally, consider user interface and ease of use, as a well-designed app can significantly improve your scanning experience. Finally, verify whether the app is free or requires a purchase and whether it includes any advertisements that might interfere with its use.
Q: What are the applications of data matrix scanners?
A: Data matrix scanners are used in a variety of applications across different industries. In manufacturing, they are used for tracking parts and assemblies throughout the production process. In logistics, data matrix codes help manage inventory by providing quick access to product information and location data. Healthcare facilities use data matrix scanners to track medications, patient information, and equipment. Retailers utilize these scanners for inventory management and point-of-sale systems. Additionally, data matrix codes are used in marketing to engage customers through promotions and interactive content. Their compact size allows for printing on small items, making them suitable for various applications.
Q: Are contactless scanners safe to use?
A: Yes, contactless scanners are generally safe to use. They operate without physical contact between the scanner and the code, which reduces the risk of contamination, especially important in healthcare and food service environments. Contactless scanning can also speed up transactions and improve user experience. However, like all technology, it is essential to ensure that the scanners are used correctly to maintain security. Users should be cautious of potential security risks, such as unauthorized access to scanned data. Adopting best practices, such as regularly updating software and using secure connections, can help mitigate these risks.
Q: How can I scan QR codes easily?
A: Scanning QR codes can be made easy by using a smartphone or tablet equipped with a camera. Most modern smartphones have built-in QR code scanning capabilities accessible through the camera app. Simply open the camera, point it at the QR code, and wait for a notification or link to appear. If you are using a dedicated QR code scanner app, open the app and follow the instructions to scan the code. Ensure that the QR code is well-lit and in focus for the best results. Practicing this process can help you become more proficient at scanning QR codes quickly and efficiently.
Q: What are the differences between various types of scanners?
A: The main differences between various types of scanners lie in their design, functionality, and intended use. Handheld scanners are portable and suitable for various environments, while fixed scanners are typically installed at checkout counters or entry points for high-volume scanning. Laser scanners are effective for reading one-dimensional barcodes, whereas imaging scanners can read both one-dimensional and two-dimensional codes. Additionally, some scanners may be equipped with advanced features, such as Bluetooth connectivity or the ability to read damaged codes, while others might be more basic. The choice of scanner will depend on the specific requirements of the user and the environment in which it will be used.
Q: How do I troubleshoot my QR code scanner?
A: Troubleshooting a QR code scanner involves several steps. First, ensure that the scanner is powered on and correctly connected to its host device. If the scanner uses batteries, check to make sure they are charged or replace them if necessary. If the scanner is not reading codes, ensure that the QR code is not damaged, obscured, or poorly printed. Adjust the distance and angle at which you are holding the scanner to the code; sometimes, moving closer or angling the scanner differently can help. If the issue persists, consult the user manual for specific troubleshooting steps or contact customer support for assistance.
Q: What are the best practices for using a barcode scanner?
A: Best practices for using a barcode scanner include ensuring that the scanner is clean and properly maintained. Regularly check for any software updates that may improve performance or security. When scanning, make sure that the barcode is well-lit and in focus, as poor lighting can hinder the scanner’s ability to read the code. Hold the scanner at the recommended distance from the barcode, and avoid any obstructions that could interfere with the scan. Additionally, train staff on the proper use of scanners to minimize errors and enhance efficiency. Finally, keep a backup of scanned data to prevent loss in case of technical issues.
Q: How can two-dimensional code scanners improve business efficiency?
A: Two-dimensional code scanners can significantly improve business efficiency by automating data entry and streamlining processes. For example, in inventory management, scanning codes can quickly update stock levels, reducing the time spent on manual counts. In retail, QR codes can speed up checkout processes, enhancing customer satisfaction. Additionally, two-dimensional codes can store more information than traditional barcodes, allowing businesses to provide customers with detailed product information or promotional offers. This can lead to better decision-making and increased sales. Furthermore, the ability to quickly analyze scanned data can help businesses identify trends and optimize operations.
Q: What should I know about scanning multiple codes at once?
A: Scanning multiple codes at once requires a scanner capable of batch scanning or multi-code reading. Not all scanners have this feature, so it is essential to choose a scanner that explicitly supports it if you need to scan multiple codes simultaneously. When scanning multiple codes, ensure that the codes are not too close together, as this can confuse the scanner. Proper lighting and a clear view of the codes will also enhance the scanning process. Some scanning applications allow you to select and process multiple codes in one action, which can save time and increase efficiency.
Q: How is scanning technology evolving?
A: Scanning technology is evolving rapidly, with advancements in software, hardware, and integration capabilities. Modern scanners are becoming more compact, faster, and capable of reading a wider variety of codes, including damaged or poorly printed codes. The emergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning is enhancing decoding accuracy and enabling advanced features such as predictive analytics and real-time data processing. Mobile device capabilities are also improving, allowing smartphones to serve as powerful scanning tools. Additionally, the integration of scanners with cloud services and other business applications is facilitating better data management and analysis, improving overall operational efficiency.
Q: What are the security risks of using code readers?
A: Security risks associated with using code readers include the potential for data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information. QR codes can be manipulated to direct users to malicious websites or to steal personal information. Users should be cautious when scanning codes from unknown sources, as these can pose phishing risks. Additionally, if a scanner is connected to a network, it may be vulnerable to hacking or malware. To mitigate these risks, businesses should implement security protocols, use trusted scanning applications, and train employees on safe scanning practices.
Q: How do I create a QR code for my business?
A: Creating a QR code for your business is a straightforward process. First, decide what information you want to encode in the QR code, such as a URL, contact information, or promotional offer. Next, use a QR code generator, which can be found online, to create the code. These generators typically allow you to input the desired data and customize the design of the QR code. Once generated, you can download the QR code image and print it on marketing materials, product packaging, or display it digitally. Test the QR code with a scanner to ensure it directs users to the correct information before widespread distribution.
Q: What is the future of barcode scanning technology?
A: The future of barcode scanning technology is likely to be shaped by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and augmented reality. We can expect scanners to become even more intelligent, with capabilities to analyze data in real-time and provide insights to businesses. The integration of scanning technology with mobile devices will continue to grow, making it more accessible and versatile. Additionally, as industries seek to improve efficiency and reduce costs, the use of automation and robotics in scanning processes may increase. Privacy and security will also play a significant role in the development of scanning technology, leading to innovations that protect user data while enhancing the user experience.
Q: How can I optimize my scanning process?
A: To optimize your scanning process, start by selecting the right scanner for your specific needs, taking into account factors such as scanning speed, accuracy, and compatibility with your existing systems. Train staff on best practices for using the scanner to minimize errors and increase efficiency. Ensure that the environment is conducive to scanning; proper lighting and organization can enhance performance. Regularly maintain and update scanning equipment to ensure it operates effectively. Additionally, analyze the data collected from scanning to identify trends and areas for improvement, which can help streamline processes further and enhance productivity.
Q: What are the common issues with digital scanners?
A: Common issues with digital scanners include connectivity problems, such as difficulty pairing with devices or unstable connections. Scanners may also struggle to read damaged or poorly printed codes, resulting in errors. Battery life can be a concern for portable scanners, necessitating frequent recharging or battery replacements. Software bugs or outdated applications can impact scanning performance and reliability. Environmental factors, such as poor lighting or obstructions, can also hinder a scanner’s ability to function effectively. Regular maintenance, updates, and proper usage can help mitigate these issues and ensure optimal performance.
Related Reports:
Integrated Delivery Network Market
https://www.statsndata.org/report/integrated-delivery-network-market-35891
Time Tagging Electrical Equipment Market
https://www.statsndata.org/report/time-tagging-electrical-equipment-market-149585
Foam Corner Protectors Market
https://www.statsndata.org/report/foam-corner-protectors-market-183830
Disposable Static Mixers Market
https://www.statsndata.org/report/disposable-static-mixers-market-81125
Drinking Water and Wastewater On-Line Water Quality Monitoring System Market
https://www.statsndata.org/report/drinking-water-and-wastewater-on-line-water-quality-monitoring-system-market-45030
John Jones
Sales & Marketing Head | Stats N Data
Email: sales@statsndata.org
Website: http://www.statsndata.org
STATS N DATA is a trusted provider of industry intelligence and market research, delivering actionable insights to businesses across diverse sectors. We specialize in helping organizations navigate complex markets with advanced analytics, detailed market segmentation, and strategic guidance. Our expertise spans industries including technology, healthcare, telecommunications, energy, food & beverages, and more.
Committed to accuracy and innovation, we provide tailored reports that empower clients to make informed decisions, identify emerging opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth. Our team of skilled analysts leverages cutting-edge methodologies to ensure every report addresses the unique challenges of our clients.
At STATS N DATA, we transform data into knowledge and insights into success. Partner with us to gain a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business environment. For more information, visit https://www.statsndata.org or contact us today at sales@statsndata.org
This release was published on openPR.