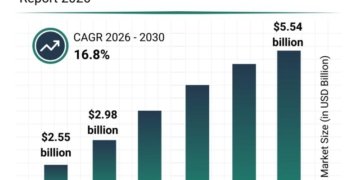
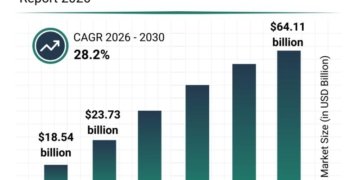
In the modern digital landscape, identity fraud is advancing rapidly, with synthetic identity fraud emerging as one of the most common and destructive types of identity theft. This type of fraud is particularly deceptive as it doesn’t involve stealing an entire identity but rather fabricating a new one by blending genuine and fake information. Fraudsters involved in synthetic identity schemes create false credit profiles, open accounts, and take out loans-all while staying under the radar. Today, synthetic identity fraud is responsible for more than 80% of all new account fraud, resulting in multi-billion-dollar losses each year.
In this article, we’ll explore what synthetic identity fraud is, how it works, how it differs from traditional identity theft, methods for detecting it, and preventive measures businesses can take using advanced ID verification https://regulaforensics.com/products/document-reader-sdk/ systems.
What is Synthetic Identity Fraud?
Synthetic identity fraud https://regulaforensics.com/blog/synthetic-identity-fraud/ occurs when criminals create a false identity by combining real, stolen personal data-such as a legitimate Social Security Number (SSN)-with made-up details like a fake name, birthdate, or address. Once created, this synthetic identity is used to apply for loans, credit cards, and other financial services. Over time, fraudsters carefully cultivate these identities, building credibility and trust within the financial system. Eventually, after gaining sufficient credibility, the fraudsters exploit the system by maxing out loans and credit limits before vanishing, leaving behind significant financial damage.
This form of fraud can go undetected for years, making it difficult to identify before substantial harm is done. Since the identity is synthetic, the fraudster can disappear without a trace, making it even more challenging for authorities or financial institutions to track them down.
How Does Synthetic Identity Theft Work?
Synthetic identity fraud follows a structured approach, allowing fraudsters to manipulate financial institutions and build a credible but entirely fake identity. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Acquisition of Real Data: Fraudsters typically start by obtaining real personal information, such as a legitimate SSN, often from vulnerable groups like children, the elderly, or deceased individuals. This data is often obtained through illegal means, including the purchase of stolen information from the dark web.
Combining Real and Fake Information: After acquiring real data, the fraudster mixes it with fabricated information-such as a fake name, birthdate, and address-to create a new synthetic identity.
Building a Credit Profile: Using the synthetic identity, the fraudster applies for loans or credit cards. Initially, they may be rejected or receive low credit limits, but as they continue to use the identity, make small payments, and build a positive credit history, their creditworthiness improves. Over time, financial institutions become more willing to extend larger credit amounts.
Exploiting the Identity: Once the synthetic identity has established a solid credit history, the fraudster capitalizes by maxing out credit cards, taking out loans, and then disappearing. Since the synthetic identity never truly belonged to a real person, the fraud becomes almost impossible to trace, leaving financial institutions to bear the financial losses.
Synthetic vs. Traditional Identity Theft
Although both synthetic and traditional identity theft involve the misuse of personal information, they operate in different ways:
Traditional Identity Theft: In traditional identity theft, a criminal steals an individual’s entire identity, including their name, SSN, date of birth, and other personal details. The fraudster then uses this stolen identity to open accounts, apply for loans, or make unauthorized purchases in the victim’s name. Victims often notice irregular activity on their accounts and can report the fraud fairly quickly.
Synthetic Identity Fraud: In contrast, synthetic identity fraud involves creating a new, fake identity by combining real and fake data. While a genuine SSN might be used, it is not associated with the individual’s real name or personal details. This form of fraud is harder to detect because no real person is actively monitoring the identity, and the financial losses are usually absorbed by businesses rather than individual consumers.
The key difference lies in the fact that synthetic identity fraud creates a fabricated person, making it more difficult for businesses to detect and mitigate the fraud.
How to Detect Synthetic Identity Fraud
Detecting synthetic identity fraud is a challenging task because fraudsters take the time to carefully build credible identities. However, businesses can still identify some red flags that may indicate fraudulent activity:
Discrepancies in Information: Synthetic identities often have inconsistencies in details like mismatched names, addresses, or birthdates. Any discrepancies between what is provided by the applicant and what is found in public records should raise suspicions.
Absence of Credit History: A newly created synthetic identity may lack a credit history altogether. However, fraudsters may gradually build this profile over time. Rapid credit-building behavior or applying for multiple credit products in a short time frame are potential signs of synthetic fraud.
Use of SSNs from Vulnerable Populations: Synthetic identities are often created using SSNs belonging to children, the elderly, or deceased individuals. Monitoring SSN usage from these vulnerable groups in credit applications can help detect fraud.
Unusual Application Patterns: Fraudsters may submit multiple credit applications using the same synthetic identity within a brief period. Identifying such patterns can signal potential fraud.
Suspicious Payment Behaviors: While synthetic identities typically make small payments to maintain good standing, sudden increases in credit usage or unusual payment patterns can indicate that a fraudster is preparing to exploit the synthetic identity.
How to Prevent Synthetic Identity Theft
Preventing synthetic identity fraud requires the use of advanced technology and robust identity verification measures. Here are several key strategies businesses can implement to safeguard against this growing threat:
Automated Identity Verification: Implementing automated ID verification systems that utilize biometric screening, document authentication, and real-time data checks is essential. Advanced solutions can quickly verify government-issued IDs and compare user-provided information with biometric data (e.g., selfies) to ensure that the applicant’s identity is genuine.
Document Authentication and Public Records Analysis: Businesses must not only verify the authenticity of government-issued documents but also cross-check them with public records. By analyzing public data, businesses can confirm that the information on the ID matches with other publicly available data. Any discrepancies may indicate synthetic fraud.
SSN Validation: Validating SSNs through official databases is a crucial step in preventing synthetic fraud. This process ensures that the SSN belongs to a real individual and has not been misused to create a synthetic identity.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): For higher-risk customers or transactions, businesses should conduct enhanced due diligence. This involves a deeper examination of the customer’s background, including their credit history, past addresses, and any linked accounts, to identify potential red flags.
Ongoing Monitoring and Fraud Detection: Because synthetic identity fraud can develop over several years, continuous monitoring of customer accounts is essential. Leveraging AI-powered fraud detection systems, businesses can track credit behaviors, identify unusual patterns, and flag suspicious activities for further investigation.
Conclusion
Synthetic identity fraud is one of the most complex and challenging forms of fraud to detect and prevent. By combining real and fake information, fraudsters create entirely new identities that appear legitimate, allowing them to build credit and exploit financial institutions for significant financial gain.
However, businesses can defend themselves by adopting advanced ID verification tools, document authentication, and public records analysis. Using cutting-edge technology to detect and prevent synthetic identity fraud not only helps businesses protect themselves from financial losses but also fosters trust in their identity verification processes.
As this type of fraud continues to rise, investing in sophisticated solutions will help businesses stay ahead of fraudsters while ensuring compliance and security across their operations.
P.O Bagarji Town Bagarji Village Ghumra Thesil New Sukkur District Sukkur Province Sindh Pakistan 65200.
Wiki Blogs News always keeps careful online users to provide purposeful information and to keep belief to provide solution based information.
This release was published on openPR.