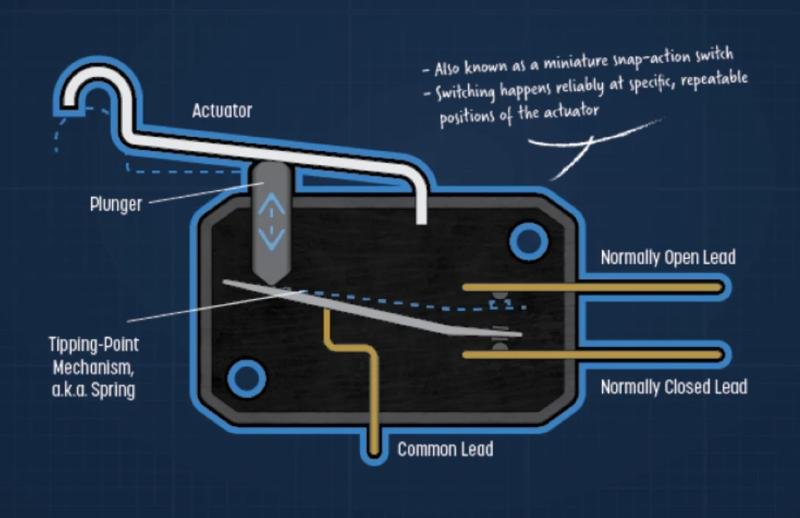
When you press a mouse button, the sensation you feel under your fingertip comes from a small part deep inside the device. This part is called a micro switch, and it does a simple but important job. It connects and disconnects an electrical circuit each time you press the button. That action tells the computer you have clicked. The way this happens affects the physical feel, the sound, and even the comfort of clicking over long sessions.
Understanding the role of the micro switch makes it easier to see why two mice with identical shapes can feel very different in use. The component beneath the button plays a large part in defining that experience, whether it is light and quiet or crisp and distinct.
The Mechanism Inside
A micro switch is a small hardware component resting on the circuit board of the mouse. When you press the button on top of the mouse, a small actuator pushes into the switch’s internal mechanism.
Within that description there are a few subtle elements that influence feel. The stiffness of the spring, the shape of the metal contacts, and even the materials chosen for those contacts shape the resistance you feel and the sound you hear with each press. Different designs create different impressions of ‘tactile’ response and rebound.
Feel and Response Defined
When people discuss click feel, they are often talking about multiple aspects. Actuation force is the amount of pressure required to press the switch. Clicking mice typically involve switches that require less pressure. A heavier click can feel intentional and strong, which can be comforting to some users. This is achieved by varying the spring tension and switch design.
Rebound speed is another consideration. The speed at which the switch resets to its original position after a click can influence the speed at which additional clicks are made. A faster rebound can make clicking feel more responsive. This is important in applications that require rapid input.
Durability is also a consideration. Good micro switches are measured in millions of cycles, which means they can withstand repeated use. Poorer switches may fail sooner, resulting in problems such as double clicks and missed button presses. Such issues are common after several years of use or under heavy loads.
Choices in Design
Not all micro switches are created equal. Conventional mechanical micro switches use metal contacts and springs. More modern versions, such as optical micro switches, use a light beam instead of metal to register the click. Such variants may alter the durability and click feel.
Even in conventional switches, the design uses variations in materials and shapes to improve the design. Gold or silver alloy contacts are resistant to corrosion and conduct electricity well. Springs and levers are designed to provide a balance between the tactile feedback and durability.
Practical Experience
For many users the difference between two mice may feel subtle at first. Over time, however, variations in micro switch design become clearer. A mouse used for office work might have a softer click that fades into the background, while a gaming mouse might produce a more pronounced sensation that keeps pace with rapid clicking. These distinctions matter most in extended or precision tasks.
Conclusion
The https://www.swiclick.com/micro-switch inside a mouse is a modest piece of hardware with a large influence on how clicking feels. It shapes the physical resistance, sound, and timing of every click you make. Through its design, choice of materials, and internal mechanics, a micro switch can make a mouse feel quick and lively or steady and quiet. Though often overlooked, this small component is central to the way we interact with computers through a device we take for granted every day
SEO MAVENS LLC
1001 S MAIN ST STE 500
KALISPELL, MT 59901
SEO Mavens is a U.S.-based digital marketing agency specializing in SEO, link building, and content strategy, helping global brands improve online visibility through ethical, data-driven search optimization.
This release was published on openPR.